Tag Archives: PID
Instrumentation for Environmental and Process Monitoring
Gas Analyzers
Gas Analyzers
Gas analyzers are critical instruments used to determine the concentration of specific gases within a given sample, whether it's ambient air, industrial emissions, or process streams. Their importance spans across environmental protection, industrial safety, process optimization, and quality control. Understanding the principles and applications of various gas analyzer technologies is fundamental for effective monitoring.
Importance of Gas Analysis:
Environmental Monitoring: Detecting and quantifying pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM) in the atmosphere to assess air quality and identify pollution sources.
Industrial Safety: Monitoring workplace environments for hazardous gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S), methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and flammable gases to prevent explosions, poisoning, and other safety incidents.
Process Control: Analyzing gas compositions in industrial processes, such as combustion, chemical reactions, and fermentation, to...
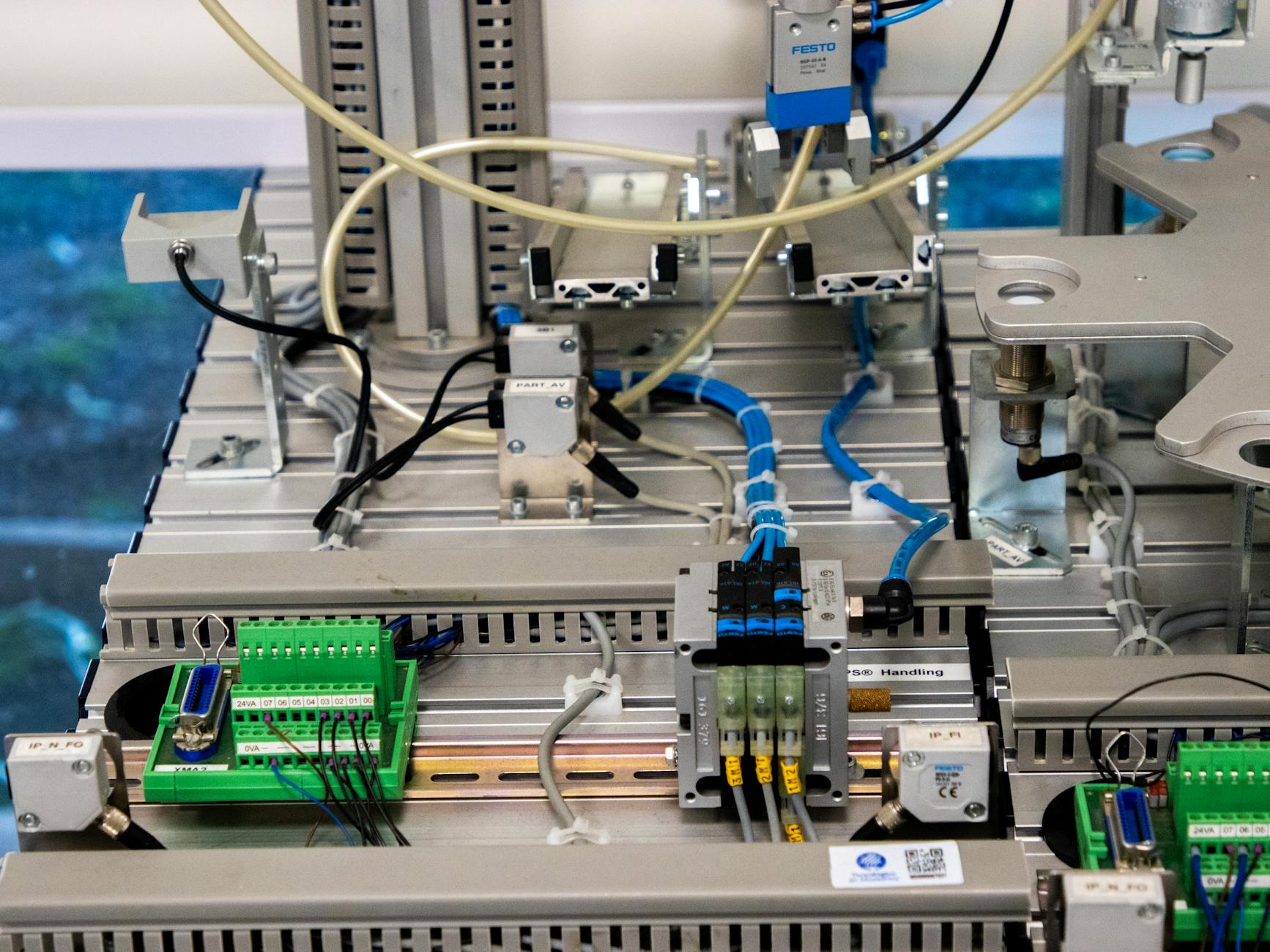
Process Control Systems
Comprehensive Overview of Process Control Systems
Process control systems refer to the methodologies and technologies employed across industries to regulate production processes, ensuring output consistency, quality, and operational efficiency. From manufacturing plants and chemical processes to power generation and pharmaceutical production, process control systems are integral in maintaining stability and reliability of numerous industrial applications. Effective process control can significantly reduce waste, enhance safety, optimise energy usage, and improve the overall profitability and sustainability of operations.
Overview of Process Control
At its core, process control systems involve measurement, comparison, calculation, and corrective action, which function collaboratively to maintain the desired level or output of any given process. Sensors measure specific parameters (such as temperature, pressure, or concentration), whereas controllers analyse data and determine necessary adjustments. Lastly, actuators carry out the commands issued by controllers, adjusting the parameters to...